Avicenna Kibana Integration
Kibana is an open-source data visualization tool which can create different graphs and charts from large amounts of data. Kibana allows you to explore the data, create visualizations such as bar chart, line charts, scatter plots, maps, and many more. You can further combine these visualizations to create interactive dashboards.
In this document, we describe how you can use Kibana to explore and visualize your Avicenna study data. This document does not intend to teach you how Kibana, Elasticsearch, or Lucine works. There are already many online resources and training videos for these technologies. We suggest you review them to better understand how you can use Kibana for your work.
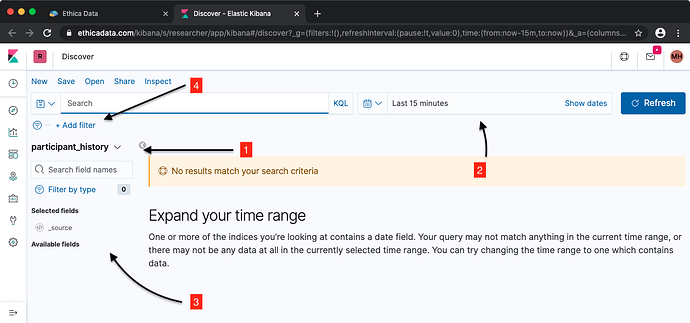
For each study you create in Avicenna, a set of data tables are created in a data storage system called Elasticsearch. These tables are also called index or index pattern. Kibana allows you to access these data tables, query them, read the data, and visualize them. To access the Kibana, go to the Researcher Dashboard, and from the left-side menu click on Kibana. This will take you to a page similar to the image below:
There are 4 important sections in the above image:
Number 1 lists the data tables for your study. Your study does not necessarily have data in all these tables, depending on which data sources and which activities you have added to your study.
Number 2 shows the time range over which you are querying the data. By default, the time range just shows the data for the past 15 minutes, so there is a chance that you do not see any data. You can increase this time range to load more data.
Number 3 lists the data fields that are available in the current data table. This list is different depending on the data table that you have selected. For example, for GPS it includes the location and the speed of the movement, while for Pedometer it includes the number of steps taken.
Number 4 allows you to filter your data. You can put filter on any data field that exist in the current data table. For example, assuming that you are looking at the Pedometer data table, you can filter data for those who have taken 100 steps or more.
[!info]
By clicking on theSharebutton at the top, you can export your data.
Avicenna does not store all data sources in the Elasticsearch. At the moment, only the following data sources are stored in the Elasticsearch and therefore are accessible through Kibana:
- GPS (
gpsindex) - Wi-Fi (
wifiindex) - Pedometer (
pedometerindex) - Motion-based Activity Recognition (
mb_activity_recindex) - Battery (
batteryindex) - Screen State (
screen_stateindex) - Bluetooth (
bluetoothindex) - Bluetooth Beacons (
beaconindex) - App Usage Statistics (
app_uageindex) - Call & SMS logs (
telephonycommsindex) - Participant Audit Logs (
participant_historyindex) - Survey Responses (
survey_responsesindex) - Stroop Responses (
stroop_responsesindex) - Time Use Diary Responses (
time_use_responsesindex) - Fitbit Activity Summary (
fitbit_daily_activityindex) - Fitbit Activity Intraday (
fitbit_activityindex) - Fitbit Sleep (
fitbit_sleepindex) - Fitbit Heart Rate (
fitbit_heart_rateindex) - WHOOP Sleep (
whoop_sleepindex) - WHOOP Workout (
whoop_workoutindex) - WHOOP Recovery (
whoop_recoveryindex)
Below you can read the details for each of these data sources, including available fields and their types.
Avicenna clusters host the services for Kibana and Elasticsearch. Therefore, your study data does not leave Avicenna servers for any of the procedures described here.
Available Data Sources
This section describes the available data sources and the fields each data source has in Kibana. The name of the field is necessary to access the field’s data in Kibana. The field’s type specifies the type of data being stored in it. You can refer to Elasticsearch’s field datatypes for more details about each type. You can also check the Data Sources section for a detailed definition of each field.
[!note]
We don’t support all data sources in Elasticsearch/Kibana because some of them have a higher load.
Common Fields
The following data fields are available in each of the data sources described below:
| Name | Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Study ID | study_id |
Integer | The ID of the study this record belongs to. |
| Participant ID | user_id |
Integer | The ID of the participant who provided this record. |
| Device ID | device_id |
Keyword | The ID of the device which provided this record. Each participant can own multiple devices during the course of the study, and each device will have a unique ID. Avicenna uses this ID to tag all records coming from the same device. The ID remains the same even when the user uninstalls and reinstalls the Avicenna app on their phone. |
| Record Time | record_time |
Date | The time which this record was captured. For survey responses, record_time for all responses in the same session are identical, and it represents the time when the user has pressed Submit button (or equivalent) to finish responding to the survey. |
| Relative Record Time | rel_record_time |
Date | The number of milliseconds between the participant’s participation period start time, and the time this record was captured. This field is particularly useful for studies with rolling enrollment, where each participant starts the study at a potentially different date. Therefore, 0 indicates the record was captured right at the start time, 1 indicates the record was captured 1 ms after the start time, and so on. Note that this field is marked as Date, therefore Avicenna will show the field as milliseconds passed Unix epoch (Jan. 1st, 1970). If you plan to query the data based on this field, you need to set the time range based on this date. |
Survey Responses
For survey responses, Avicenna stores each response to a given question as a separate record. Therefore, a given survey session can contain multiple records. For example, assume your survey contains 5 questions, from question ID 1 to 5. Every time a participant responds to your survey, 5 new records will be added to this index, one for each question (assuming the participant has responded to all questions).
Also, note that not each record contains all the fields specified here. If a given record does not have a given field, it means the field was not relevant for that record. For example, if a survey response is of type text, the record will contain answer_content, but it will not contain answer_url.
Index name: survey_responses
Index fields (see Common Fields too):
| Name | Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Survey ID | survey_id |
Integer | |
| Question Set ID | questionset_id |
Integer | |
| Response Duration | duration |
integer | In minutes. |
| Scheduled Time | scheduled_time |
Date | For Time- and Proximity-Triggered sessions, this shows the time the survey was automatically triggered. For User Triggered sessions, this shows the time the survey was started by the participant. |
| Prompt Time | prompt_time |
Date | Same as Scheduled Time. |
| Response Time | resp_time |
Date | The time this response was provided. |
| Iteration | iteration |
Integer | |
| Loop Count | loop_count |
Integer | |
| Question ID | q_id |
Integer | |
| Question Content | q_content |
Text | |
| Question Type | q_type |
Keyword | |
| Answer ID | answer_id |
Integer | |
| Answer Content | answer_content |
Text | |
| Answer URL | answer_url |
Keyword | |
| Location | location |
Geo Point | |
| Location Accuracy | location_accu |
Double | |
| Location Speed | location_speed |
Double | |
| Preferred Unit | pref_unit |
Keyword | |
| Selector | selector |
Keyword |
Device State
The Device State logs are utilized to convey various states and settings of participants’ Android and iOS devices running the Avicenna native app. They provide a holistic view of the device’s operational status, covering aspects from battery life to connectivity. New reports are created as soon as one of the fields changes its value. For example, if the power saving mode is enabled, a new report is created that includes the new value of the power saving mode field and the latest values of other fields.
Index name: device_state
Index fields (see Common Fields too):
| Name | Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Status | battery_status |
Keyword | A battery level below 15% is considered LOW. Values: UNKNOWN = 0, OK = 1, LOW = 2 |
| Battery Level | battery_level |
Integer | Shows the current battery level as a percentage (0-100%). The app will check for updates on this field if any other field changes (not upon battery level changes). |
| Power Saving Mode | power_saving_mode |
Keyword | Values: UNKNOWN = 0, Enabled = 1, Disabled = 2 |
| Battery Optimization | battery_optimization |
Keyword | Android only. Values: UNKNOWN = 0, Enabled = 1, Disabled = 2 |
| Power Connectivity | is_power_connected |
Keyword | Indicates whether the device is currently connected to a power source. Values: UNKNOWN = 0, Enabled = 1, Disabled = 2 |
| Storage Status | storage_status |
Keyword | Android only. Provides information about the device’s internal storage status. OK and LOW values depend on the device’s specifications and system reports. Values: UNKNOWN = 0, OK = 1, LOW = 2 |
| Memory Status | memory_status |
Keyword | Android only. Reports the status of the device’s RAM usage. Avicenna checks the memory status every 15 minutes alongside the OS notifications regarding low memory conditions. OK and LOW values depend on the device’s specifications and system reports. Values: UNKNOWN = 0, OK = 1, LOW = 2 |
| Network Connection type | network_connection_type |
Keyword | Values: UNKNOWN = 0, NOT_CONNECTED = 1, CELLULAR = 2, WIFI = 3 |
| Airplane Mode | airplane_mode |
Keyword | Android only. Values: UNKNOWN = 0, Enabled = 1, Disabled = 2 |
| Do Not Disturb Mode | do_not_disturb |
Keyword | Android only. Values: UNKNOWN = 0, Enabled = 1, Disabled = 2 |
| Locale | locale |
Keyword | |
| Time Zone | timezone |
Keyword | |
| Operating System Version | os_version |
Keyword |
[!info]
After the participant logs in to the Avicenna native app on their iOS and Android devices, all fields will be initialized with their current state one by one, and each initialization will generate a new log. Until these fields get updated with their actual initial state, their value will beUNKNOWNin the logs.
Application State
The Application State logs report various states and settings of participants’ Android and iOS apps. They provide a holistic view of the application’s status. New reports are created as soon as one of the fields changes its value. For example, if the app language changes, a new report is created that includes the new value of the language field and the latest values of other fields.
Index name: application_state
Index fields (see Common Fields too):
| Name | Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Email Notifications | email_notifications |
Keyword | Indicates whether email notifications are enabled or disabled in the application settings. Values: UNKNOWN, ENABLED, DISABLED |
| SMS Notifications | sms_notifications |
Keyword | Indicates whether SMS notifications are enabled or disabled in the application settings. Values: UNKNOWN, ENABLED, DISABLED |
| Wi-Fi Only Upload | wifi_only_upload |
Keyword | Specifies whether data uploads are restricted to Wi-Fi connections only in the application settings. Values: UNKNOWN, ENABLED, DISABLED |
| Allow Data Collection | allow_data_collection |
Keyword | Denotes whether data collection is permitted by the participant in the application settings. Values: UNKNOWN, ENABLED, DISABLED |
| Language | language |
Keyword | The current language of the application set by the participant. |
| App Version Number | app_version_number |
Integer | The current version number of the application. |
| Execution Mode | exec_mode |
Keyword | Indicates the execution mode of the application. Values: UNKNOWN, BACKGROUND, FOREGROUND, TERMINATED (only iOS supports this value and it will be logged only when the participant, not the OS, terminates the app) |
| Execution Mode Change Occurred At | exec_mode_change_occured_at |
Date | Timestamp of the last time the execution mode has changed. |
| Onboarding Alerts | onboarding_alerts |
Nested | A list indicating changes in alerts related to app permissions and settings that may require user attention or action. Each alert is defined with a type (see the next tables) and status (Values: UNKNOWN, Added which means the alert showed up on the app, Deleted which means the alert was taken care of by the participant in some way). |
| Study Data Sources | study_datasources |
Nested | A list indicating whether data sources are enabled/disabled. Each data source is defined with a type (see the next tables) and status (Values: UNKNOWN, Enabled, Disabled). |
| Survey Notifications | survey_notifications |
Keyword | Android only. Indicates the status of survey notifications. Values: UNKNOWN, ENABLED, DISABLED |
| Sticky Notifications | sticky_notifications |
Keyword | Android only. Indicates the status of sticky notifications. Values: UNKNOWN, ENABLED, DISABLED |
[!info]
After the participant logs in to the Avicenna native app on their iOS and Android devices, all fields will be initialized with their current state one by one, and each initialization will generate a new log. Until these fields get updated with their actual initial state, their value will beUNKNOWNin the logs.
| Onboarding Alerts Types | Description |
|---|---|
| Unknown | |
| GPS | To grant the app permission to collect GPS data. Also, on iOS devices, with GPS permission, Avicenna can keep the app open in the background for a longer time. |
| Activity Recognition | To grant the app permission to collect motion sensor data. |
| App Usage | To grant the app permission to collect app usage data. |
| Bluetooth | To turn the Bluetooth on. |
| WiFi | To turn the WiFi on. |
| Garmin | To grant Avicenna permission to access Garmin data. |
| Fitbit | To grant Avicenna permission to access Fitbit data. |
| WHOOP | To grant Avicenna permission to access WHOOP data. |
| HealthKit | iOS only. To grant Avicenna permission to access HealthKit data. |
| SensorKit | iOS only. To grant Avicenna permission to access Sensor data. |
| Audio Capture | To grant the app permission to record audio from the microphone. |
| Background App Refresh | iOS only. To enable background app refresh. |
| Time-Sensitive Notification | iOS only. To enable time-sensitive notifications. |
| Persistent Notification Banner | iOS only. To enable the persistent notification banner. |
| Phone Validation | To verify the phone number. |
| Email Validation | To verify the email address. |
| Application Update | To notify when a new app version is available on the store. |
| Location Service | To enable the Location service. |
| Notifications | To grant the app permission to prompt notifications. |
| Battery Optimization | Android only. To disable battery optimization. |
| Battery Optimization (Device Specific) | Android only. To disable battery optimization if the device is “Sony”, “Samsung”, “Huawei”, “Xiaomi”, or “Oneplus”. |
| Schedule Alerts | Android only. To grant the app permission to schedule notifications and alarms. |
| Study Data Sources Types |
|---|
| Unknown |
| Accelerometer |
| Ambient Temperature |
| Gyroscope |
| Gravity |
| Light |
| Linear Accelerometer |
| Magnet |
| Orientation |
| Pressure |
| Proximity |
| Relative Humidity |
| WiFi |
| Bluetooth |
| GPS |
| Battery |
| Ambient Noise |
| Ambient Audio |
| App Usage |
| Screen State |
| Pedometer |
| Motion Based Activity Recognition |
| Beacon |
| Apple HealthKit |
| Apple SensorKit |
| Fitbit |
| Garmin |
| WHOOP |
GPS
Index name: gps
Index fields (see Common Fields too):
| Name | Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provider | provider |
Keyword | |
| Satellite Time | satellite_time |
Date | |
| Location | location |
Geo Point | |
| Speed | speed |
Double | |
| Accuracy | accu |
Double | |
| Altitude | alt |
Double | |
| Bearing | bearing |
Double |
Wi-Fi
Index name: wifi
Index fields (see Common Fields too):
| Name | Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSID | ssid |
Keyword | |
| BSSID | bssid |
Keyword | |
| Access Point Capabilities | capabilities |
Keyword | |
| Frequency | freq |
Integer | |
| Level | level |
Integer |
Pedometer
Index name: pedometer
Index fields (see Common Fields too):
| Name | Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steps | steps |
Integer | |
| Accuracy | accu |
Double | |
| Distance | distance |
Double | |
| Average Active Pace | avg_active_pace |
Double | |
| Current Cadence | cur_cadence |
Double | |
| Current Pace | cur_pace |
Double | |
| Duration | duration |
Integer | |
| Floor Ascended | floor_ascended |
Double | |
| Floor Descended | floor_descended |
Double |
Motion-based Activity Recognition
Index name: mb_activity_rec
Index fields (see Common Fields too):
| Name | Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Activity Type | activity_type |
Integer | |
| Confidence Level | confidence_level |
Integer |
Battery
Index name: battery
Index fields (see Common Fields too):
| Name | Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level | level |
Integer | |
| Scale | scale |
Integer | |
| Status | status |
Integer | |
| Plugged | plugged |
Integer | |
| Temperature | temperature |
Integer | |
| Voltage | voltage |
Integer |
Screen State
Index name: screen_state
Index fields (see Common Fields too):
| Name | Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Screen State | state |
Boolean | |
| End Time | end_time |
Date |
Bluetooth
Index name: bluetooth
Index fields (see Common Fields too):
| Name | Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAC Address | mac |
Keyword | |
| Device Name | dev_name |
Keyword | |
| Device Class | dev_class |
Keyword | |
| RSSI | rssi |
Integer |
Bluetooth Beacons
Index name: beacon
Index fields (see Common Fields too):
| Name | Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAC Address | mac |
Keyword | |
| Device Name | dev_name |
Keyword | |
| Device Class | dev_class |
Integer | |
| Payload | payload |
Long | |
| Team ID | team_id |
Integer | |
| Role ID | role_id |
Integer | |
| Subject ID | subject_id |
Integer | |
| RSSI | rssi |
Integer |
App Usage
Index name: app_usage
Index fields (see Common Fields too):
| Name | Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| App Name | app_name |
Keyword | |
| Start Time | start_time |
Date | |
| End Time | end_time |
Date | |
| Last Used | last_used |
Date | |
| Foreground Time | foreground_time_ms |
Integer | In milliseconds. |
Troubleshooting
I can’t log in to Kibana
If you’re seeing an “Invalid username or password” error when trying to access Kibana, try these steps:
- Access Kibana through the researcher dashboard. Instead of going directly to the Kibana URL, first log in to the researcher dashboard, then click on the Kibana button from the sidebar menu. This should automatically authenticate you.
- Clear browser cookies. If the above doesn’t work, try clearing all cookies related to the
avicennaresearch.comdomain in your browser, then log in to the researcher dashboard again and access Kibana from there. - Log out and log back in. Sometimes logging out of the researcher dashboard completely and logging back in before clicking the Kibana button can resolve authentication issues.
Date/time values in Kibana seem off by a few hours
When viewing date/time values in Kibana, you may notice some of those values appear off by a few hours from what you expect, while some others are always in UTC (e.g., the date/time values in the Message field under the Audit Trail). That’s because Kibana guesses the browser’s timezone and adjusts the standalone UTC date/time fields to that timezone. Note that Avicenna stores almost all date/time values in UTC, but the Kibana configuration may change those to your local timezone.
To resolve this issue, you can do one of the following:
- Export the data via the researcher dashboard and analyze it in third-party software.
- Use a browser extension to force the UTC timezone. This ensures consistency between Kibana’s date/time fields and text-based fields that may contain date/time values (e.g., Audit Trail’s Message).
Also, if you want to use the participant’s local timezone, you can still use a browser extension to force that timezone, but note that:
- Text-based fields that may contain date/time values won’t automatically align with the timezone you set, and
- You’ll need to cross-reference the audit logs for timezone change events and manually adjust time zones for periods between those events.